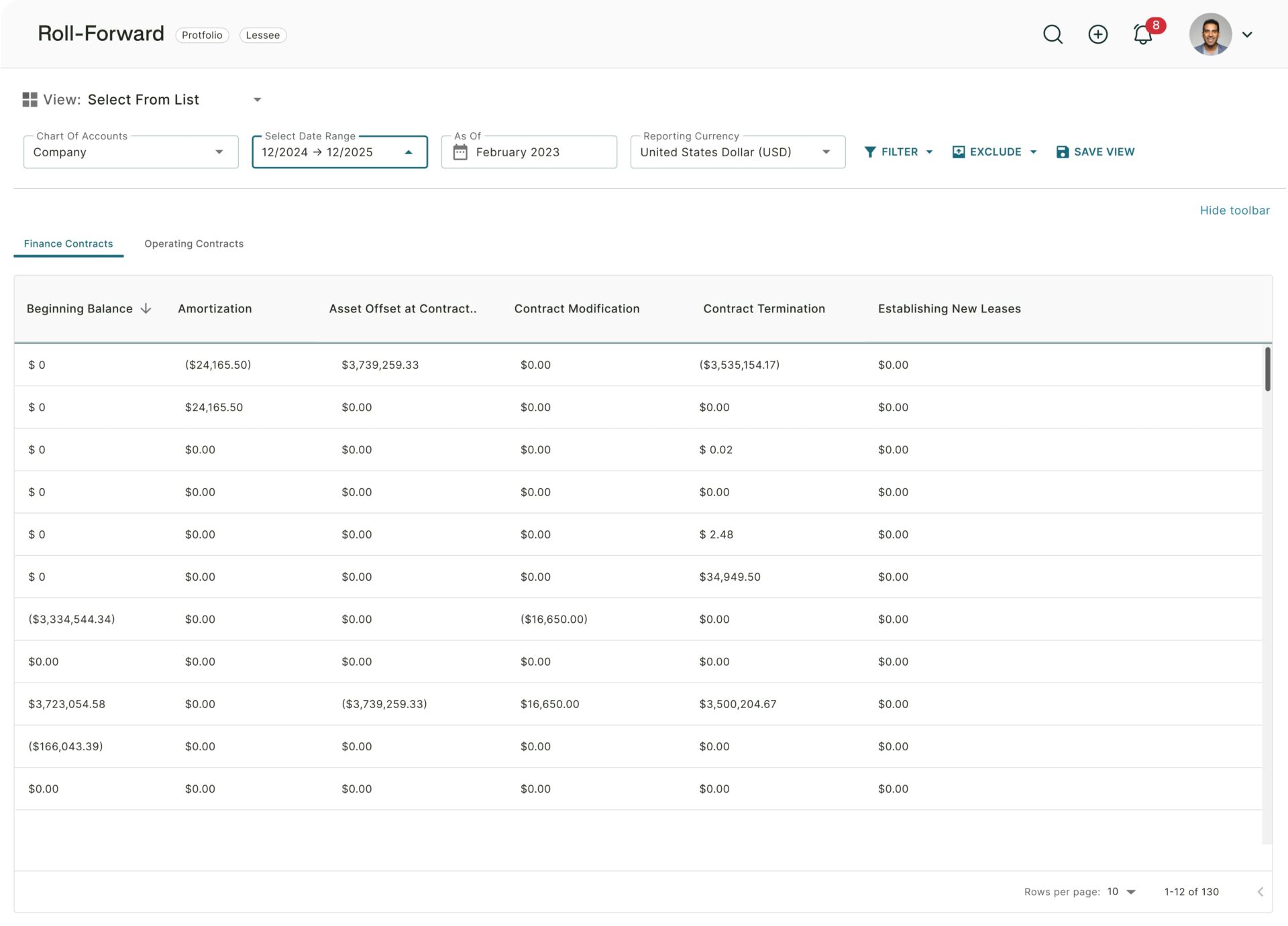
Advances in AI and automation have given auditors more tools than ever to validate financial data. But auditors are only one half of the equation.
A quality audit trail is the foundation of trust. It’s the connective tissue between raw source documents, the accounting system, and the final financial statements. When the trail is fragmented or buried in inboxes, even the most sophisticated workflow turns into a scavenger hunt.
As compliance demands grow, transactions become more complex, and expectations for transparency increase, audit trails matter more than ever. The good news is that the same AI transforming reporting can transform audit trails, too.
In this guide, we’ll cover what an audit trail is, why it matters, what it should include, and how platforms like Trullion help build modern, audit-ready workflows without the manual overhead.
What is an audit trail?
At its core, an audit trail is a chronological record of financial activity: the who, what, when, where, and why behind every transaction or change. Done well, it lets any reviewer reconstruct events quickly and confidently.
A modern audit trail typically includes:
- User attribution (who): Secure identifiers for every person or system taking action
- Timestamps (when): Exact date and time of each step
- Defined actions (what): Creation, modification, approval, deletion, and so on
- Before/after values: The original and updated values for all modifications
- Linked documentation (why): Every action should include the reason for the action, including any approvals, supporting files, source contracts, invoices, or receipts
If this sounds like a lot of detail, that’s because it is. Audit trails need to be detailed enough to demonstrate transparency and accuracy, even years after the transaction happened.
Manual vs. automated audit trails
Manual audit trails rely on manually tracking activity across spreadsheets, email threads, and shared drives. They’re slow, error-prone, and nearly impossible to maintain at scale.
Email is a classic example. Many companies still store approvals, invoices, and POs in individual inboxes. When audit time comes, someone inevitably searches for missing attachments through hundreds of old emails – or discovers that critical data disappeared when a team member offboarded.
Automated audit trails eliminate this fragility. They capture activity in a centralized database in real time. AI records changes, logs documentation, and flags anomalies. Instead of stitching together breadcrumbs, finance teams get the full story the moment it happens.
The shift from manual reconstruction to automated traceability is one of the highest-leverage operational upgrades that modern accounting teams can make.
Why are audit trails important?
Accurate audit trails aren’t administrative artifacts. They’re the core infrastructure for a healthy finance function.
- Regulatory compliance: SOX, GAAP, IFRS, and industry frameworks require explicit or implied auditability. Automated audit trails help teams demonstrate compliance without last-minute scrambles.
- Fraud prevention and detection: High-quality audit logs expose anomalies quickly. Transparent audit trails also act as a natural deterrent, reducing the opportunity for misuse.
- Data integrity and accuracy: Most anomalies stem from human error. Automated audit trails validate data as it enters the system, preventing errors from cascading in the first place.
- Streamlined audits: Audit trails reduce sampling, speed up walkthroughs, and give auditors direct access to the evidence they need.
Operational transparency: Real-time visibility into changes builds trust with leadership, boards, investors, and auditors. This enables faster decision-making and stronger internal controls.
Types of audit trails
Audit trails take different forms depending on the workflow. Common categories include:
- Transaction audit trails: Track amounts, dates, payees, and approvals for validating financial statements
- System audit trails: Log system-level actions such as logins, permission changes, and configuration edits to help IT, security, and compliance teams monitor access and behavior
- Data modification audit trails: Monitor field-level edits to sensitive and operational data
- Document audit trails: Frequently used in electronic signature workflows, which capture when a document was signed, by whom, and on which device
- Consolidated audit trail (CAT): A regulatory system tracking billions of daily securities transactions in the US – one of the most complex traceability systems in finance.
What should be included in an audit trail?
Beyond the essentials mentioned earlier – user ID, timestamp, action, before/after values, and documentation – you should expect several best practices.
Security requirements
- Entries must be tamper-proof.
- Logs should be immutable, with no ability to delete historical activity.
- Access should be role-based and encrypted.
Content and data management
- Store documentation in one centralized system.
- Standardize formats and naming conventions.
- Ensure logs are searchable and exportable.
- Back up data at routine intervals, according to regulatory requirements.
Audit trail examples
Let’s look at three real-world scenarios where automated audit trails materially improve accuracy and speed.
1. Purchase order (PO) process
In many organizations, PO approvals live in siloed systems or in scattered emails. Automation centralizes the workflow:
- Purchase request submitted: Record is automatically logged with requester, timestamp, and documentation
- PO created: Terms, pricing, and vendor details are recorded
- Goods received: Receipt is verified and linked to the original documentation
- PO closed: Three-way match is completed with all financial impacts stored in the audit trail
2. Lease accounting modification
Lease accounting creates one of the most complex audit environments, especially under ASC 842 and IFRS 16.
Eisai, a pharmaceutical company with 700+ vehicle leases and nearly 50 real estate leases, struggled to track changes and reconcile data across GAAP and IFRS. Manual spreadsheets made audits difficult.
Using Trullion’s AI-powered lease accounting, Eisai implemented:
- Automated monthly audit trails
- Real-time reconciliation
- Linked documentation across every lease
- Automated journal entries
- Instant reporting for their corporate parent
Financial statement adjustments
Ahead of major events like fundraising or an acquisition, companies often make necessary adjustments to their financial statements. With automated audit trails:
- Every adjustment includes user, timestamp, rationale, and before/after values.
- Stakeholders collaborate in one shared system.
- Executives can confidently present numbers backed by transparent evidence.
How technology simplifies audit trails
Modern accounting platforms go beyond record-keeping. They turn auditability into an always-on function.
- Automated documentation: AI captures and stores activity as it happens – no manual tracking, no missing files.
- Continuous compliance monitoring: Systems evaluate changes against compliance rules in real-time.
- AI-powered anomaly detection: Machine learning flags deviations, unusual behaviors, and subtle patterns that manual reviewers often miss. It can also analyze entire data sets, instead of just samples.
- Audit-ready exports and reports: AI summarizes audit trails, generates reports, and prepares documentation in minutes for human expert review.
When evaluating modern audit trail solutions, look for:
- Automated change logs
- Data lineage visualization
- Integration with ERP and accounting tools
- Secure, role-based access
- Linked, source-level documentation
How Trullion helps teams build better audit trails
Trullion was built to give accounting and audit teams accuracy, transparency, and real-time visibility – without extra manual work:
- Linked data transparency: Every journal entry, contract, and disclosure links back to the source document.
- Automated compliance tracking: Audit trails are generated automatically across all workflows.
- Real-time audit visibility: Teams see exactly how and when data changes.
- AI-powered accuracy: Trullion eliminates manual reconciliation errors and dramatically accelerates month-end close and audit prep time. Many customers reduce weeks of effort to hours.
Trullion’s capabilities span core areas like lease accounting and audit workflows, helping teams embed auditability directly into their daily processes.
Turn audit trails into a strategic advantage
A great audit is a partnership between companies and auditors, and the quality of the audit trail determines the quality of that partnership.
Modern, automated audit trails make data more accurate, audits faster, compliance easier, and organizations more trustworthy. They form the backbone of transparency in today’s operations.
With Trullion, teams can finally automate the audit trail from source documents to disclosures, with AI validating, linking, and monitoring every step. Our on-demand webinar, The New Era of Audit, breaks down the tools and strategies leading teams are using today.