What is FRS 102?
On 27 March 2024, the Financial Reporting Council (FRC) – the body responsible for financial reporting in the UK and the Republic of Ireland – unveiled significant amendments to FRS 102 as part of its second periodic review of financial reporting standards.
FRS 102 is the comprehensive financial reporting standard applicable in areas governed by the FRC, and is designed to bring UK GAAP for private entities in line with international financial reporting standards. These changes, therefore, are expected to affect almost 3.5 million businesses.
The FRS 102 Changes
The amendments, effective for periods beginning on or after 1 January 2026 (early adoption is permitted), aim to enhance transparency, comparability, and the overall quality of financial reporting.
Key sections affected by the changes include:
1. Section 20: Leases
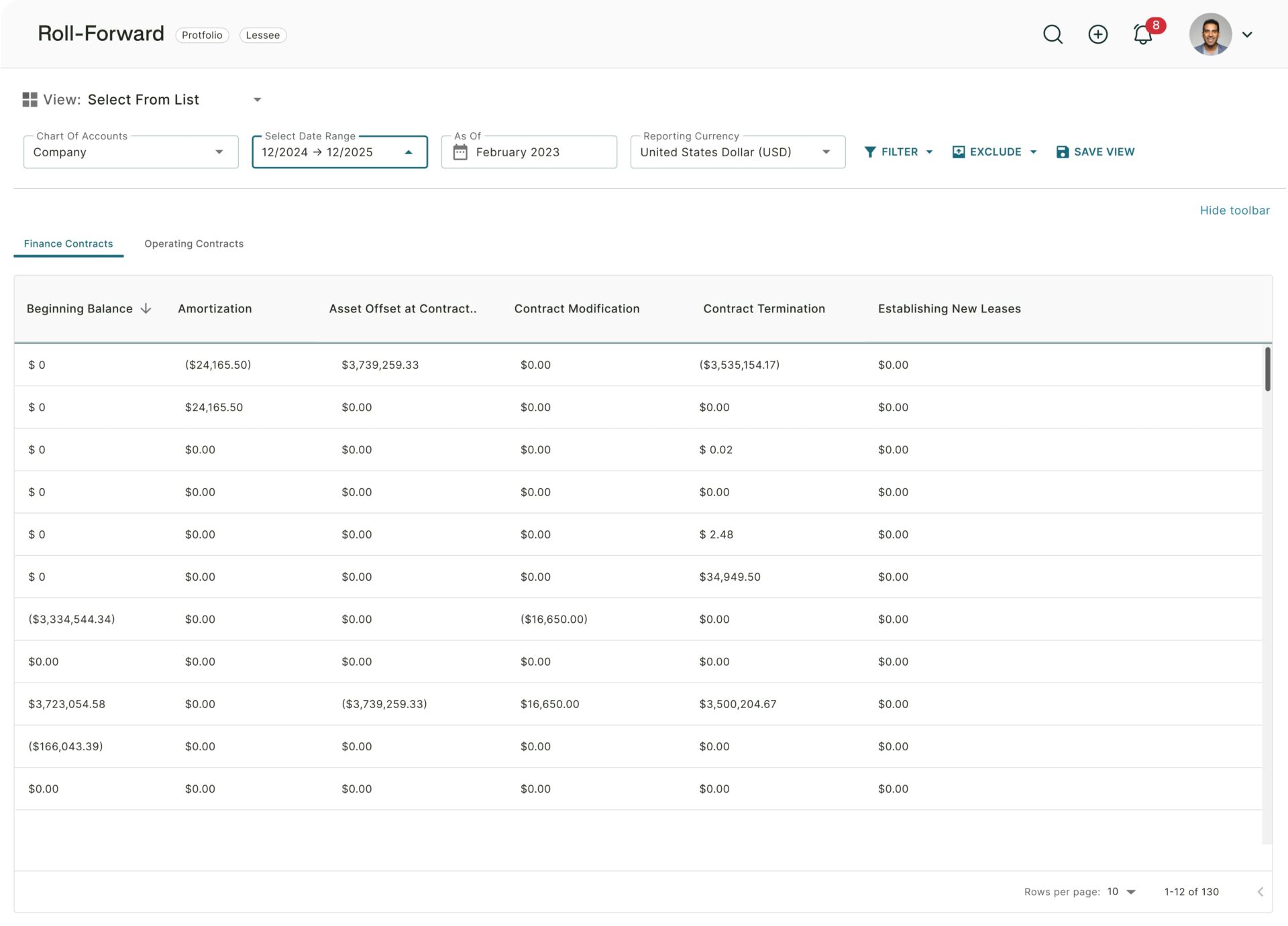
The distinction between operating and finance leases has been eliminated for lessees, leading to a broader recognition of leases as assets and liabilities on the balance sheet, akin to the existing treatment of finance leases – and much like the current IFRS 16 treatment.
However, exemptions for short-term and low-value asset leases allow such leases to remain off the balance sheet.
Compared to IFRS 16 Leases, FRS 102 adopts a higher threshold for low-value assets, reducing the number of leases that preparers need to recognize on the balance sheet.
Expected benefits of this change:
- Improved financial information through enhanced transparency
- More relevant details about assets and liabilities accurately reflect the economics of significant lease arrangements
- Potentially improved access to capital
- Consistency with international accounting principles, enhancing comparability
2. Section 23: Revenue from Contracts with Customers
A unified five-step model for recognizing revenue from customer contracts is introduced, focusing on the identification of specific goods or services promised to the customer and determining the corresponding consideration the entity is entitled to receive.
The amendment sets out the process as follows (23.4):
- Step 1: Identify the contract(s) with a customer
- Step 2: Identify the performance obligations in the contract
- Step 3: Determine the transaction price
- Step 4: Allocate the transaction price to the performance obligations in the contract
- Step 5: Recognize revenue when (or as) the entity satisfies a performance obligation
Expected benefits of this change:
- Simplified process for entities to accurately and uniformly account for revenue transactions
- Enhanced reliability and utility of information regarding the nature, amount, and timing of revenue and cash flows from customer contracts
- Potentially improved access to capital
- Consistency with international accounting principles, enhancing comparability
3. List of Other FRS 102 Sections Affected
There are also some incremental changes to other areas of FRS 102.
| FRS 102 Section | Major Changes | Expected Benefits |
| Section 1A: Small Entities | Clarity is enhanced for UK small entities on required disclosures for a true and fair view according to law. | Simplifies for UK small entities the decision-making on necessary disclosures, enhancing consistent, high-quality reporting. |
| Section 2: Concepts and Pervasive Principles | Updated for alignment with the most recent international frameworks. | Sets a basis for ongoing alignment internationally, offering benefits like increased consistency and comparability. |
| Section 2A: Fair Value Measurement | Definitions updated to match the latest international standards, with more guidance provided. | Fundamental in accounting for certain transactions, fair value measurement requires judgment. New guidance aids in achieving consistent and appropriate valuations. |
| Section 7: Statement of Cash Flows | Introduction of new disclosure requirements regarding supplier finance arrangements, effective from 1 January 2025. | Responds to the need for more information on such arrangements, ensuring consistency with international reporting standards. |
| Section 26: Share-based Payment | Enhanced guidance to assist in applying principles in specific scenarios. | Meets the demand for additional guidance and ensures alignment with international reporting standards. |
| Section 29: Income Tax | New guidance introduced for handling uncertain tax positions. | Offers further assistance to preparers tackling uncertain tax positions, ensuring alignment with international standards. |
| Section 34: Specialised Activities | Enhancements and clarifications address existing requirements and adapt to other amendments. | Makes it simpler for preparers to comprehend and adhere to requirements. |
FRS 102 Compliance: What You Need to Know
As has been seen with companies that had to comply with IFRS 15 and IFRS 16, the changes brought about by these amendments are significant.
FRS 102 Revenue Recognition
For example, when it comes to revenue recognition, entities must reassess their contract terms and how they account for revenue, potentially leading to changes in the timing and amount of revenue recognized.
FRS 102 Lease Accounting
For leases, this change could impact businesses’ reported assets and liabilities, affecting key financial ratios and possibly even debt covenants.
The main takeaway for companies already accounting for leases and revenue according to the new standards is that traditional ways of managing leases and revenue are becoming increasingly untenable.
With this added complexity, a purpose-built technological solution is key – one that leverages automation and AI to ensure accuracy and compliance.
To discuss your business’ needs in this regard, reach out to Trullion today. Trullion is the solution of choice for companies dealing with the new realities of revenue recognition and leases, and takes the headache out of dealing with these areas, saving you time while empowering you and your team to focus on high-impact activities.
FAQ: Amendments to FRS 102
- What are the major changes introduced by the FRS 102 amendments?
The amendments include significant changes, such as the elimination of the distinction between operating and finance leases, leading to a broader recognition of leases on the balance sheet. A unified five-step model for revenue recognition has been introduced for contracts with customers. Additionally, there are updates across various sections including small entities disclosures, fair value measurement, supplier finance arrangements, share-based payments, income tax, and specialized activities.
- When will the amendments to FRS 102 take effect?
The amendments are effective for accounting periods beginning on or after 1 January 2026. Early adoption is permitted.
- How do the amendments to FRS 102 impact lease accounting?
The distinction between operating and finance leases for lessees has been removed. More leases will now be recognized on the balance sheet as assets and liabilities, similar to finance lease accounting. However, exemptions for short-term and low-value asset leases allow them to remain off the balance sheet.
- What is the new revenue recognition model introduced by the amendments?
A comprehensive five-step model for recognizing revenue from customer contracts is introduced. This model focuses on identifying specific goods or services promised to customers and determining the corresponding consideration the entity is entitled to receive.
- Are there any exemptions provided in the amendments?
Yes, there are exemptions, notably for short-term and low-value asset leases, which allow such leases to remain off the balance sheet.
- What benefits are expected from these amendments?
Benefits include improved financial information transparency, more relevant details about assets and liabilities, potentially improved access to capital, and greater consistency with international accounting principles.
- How should entities prepare for these changes?
Entities should review their current accounting practices, assess the impact of the amendments on their financial reporting, and consider a software-based solution to deal with this new era.