Audit tracing and vouching are two fundamental procedures in financial auditing. They help auditors ensure the accuracy, completeness, and validity of financial records. While tracing verifies the completeness of recorded transactions, vouching confirms their legitimacy and authenticity. Together, these methods form the backbone of a reliable audit process.
Purpose of the Guide to Audit Tracing and Vouching
This guide provides an in-depth comparison of audit tracing and vouching, detailing their processes, applications, best practices, challenges, and modern technology-powered solutions.
It serves to give both auditors and non-auditors alike a deeper understanding of these procedures, and to enhance the efficiency and accuracy of audit engagements.
Understanding Audit Tracing
What is Audit Tracing?
Audit tracing is the process of following a transaction from its source documentation to the accounting records. The primary objective is to verify the completeness of financial transactions and ensure that all relevant records are included in financial statements.
How Audit Tracing Works
To ensure accuracy, auditors follow a structured approach when conducting audit tracing. First, they identify source documents such as invoices, receipts, or contracts. Next, they follow the transaction through the company’s accounting system, confirming that it is recorded accurately in the financial statements. Finally, they ensure that no transactions are left out, verifying that the financial records comprehensively reflect all business activities.
Consider an auditor reviewing a company’s payroll expenses. The auditor begins by selecting employee timecards as the source documents. They then trace these timecards through the payroll system, verifying that the corresponding salaries were recorded correctly in the general ledger and then accurately reflected in the financial statements.
Key Focus Areas in Audit Tracing
A key focus in audit tracing is the concept of completeness. Ensuring completeness of transactions is crucial, as any missing records can lead to financial discrepancies, or may be symptomatic of wider issues, such as non-functioning processes and controls. Auditors must verify that all relevant financial statements include necessary records, and identify missing or incomplete entries that could impact the overall accuracy of financial reporting.
Tools and Techniques for Audit Tracing
Various tools assist in the tracing process. Audit software helps automate data validation, while data analytics identify discrepancies that could signal errors or omissions. Additionally, auditors conduct manual reviews of financial documents to ensure completeness and reliability.
Understanding Audit Vouching
What is Vouching?
Vouching is the process of reviewing supporting documents to validate the authenticity and accuracy of recorded transactions. The goal is to ensure that every entry in financial records is legitimate and supported by verifiable documentation.
How Vouching Works
To perform vouching effectively, auditors begin by selecting transactions from the accounting records. They then retrieve corresponding supporting documents such as invoices, contracts, or receipts. After reviewing these documents, they verify that the details in the source document match the financial record and confirm that transactions comply with accounting standards and policies.
Suppose an auditor is verifying a company’s purchase transactions. They start by selecting a recorded expense entry for office supplies, for example, in the financial statements. The auditor then retrieves the corresponding supplier invoice and purchase order to confirm that the transaction actually took place, the expense was legitimate, and the recorded amount matches the supporting documents. This process ensures the accuracy and authenticity of the transaction
Key Focus Areas in Vouching
The primary focus of vouching is to ensure transactions are genuine and supported by documentation. This helps in detecting fraudulent or fictitious transactions that may distort financial records. Additionally, auditors verify that transactions comply with internal and external regulations to maintain accuracy and credibility.
Tools and Techniques for Vouching
Auditors rely on various techniques to perform vouching effectively. Document review and physical inspection help confirm the presence of supporting records. Third-party verification provides an extra layer of credibility by cross-checking information with external sources. AI-driven tools enhance fraud detection by identifying anomalies in transaction patterns.
Vouching vs. Tracing: Key Differences
Feature: Direction
Tracing: Source document → Accounting record
Vouching: Accounting record → Source document
Feature: Purpose
Tracing: Ensuring completeness of records
Vouching: Validating authenticity and accuracy
Feature: Application
Tracing: Checking if transactions are recorded
Vouching: Ensuring transactions are legitimate
Feature: Common Use
Tracing: Sales, purchases, payroll completeness checks
Vouching: Expense verification, fraud detection
When to Use Tracing and Vouching in an Audit
When to Use Tracing
Tracing is used when auditors need to ensure the completeness of transactions. This is especially useful in audits focused on verifying that no transactions are omitted, such as purchases, sales, and payroll.
When to Use Vouching
Vouching is necessary when validating the legitimacy and accuracy of transactions recorded in financial records. This method ensures that all recorded entries are supported by actual, verifiable documents such as invoices and receipts.
Integrating Tracing and Vouching
A comprehensive audit process combines both methods. For example, auditors may trace transactions to ensure completeness and then vouch for their legitimacy. This dual approach minimizes risks and enhances audit reliability by confirming both completeness and authenticity.
Best Practices for Audit Tracing and Vouching
Best Practices for Audit Tracing
To maximize effectiveness, auditors should maintain thorough documentation of all traced transactions. Using automated tools enhances accuracy and efficiency, reducing the potential for human error. Regularly reviewing and updating audit procedures ensures that all areas of concern are adequately covered.
Best Practices for Vouching
For vouching to be effective, auditors must conduct procedures consistently and thoroughly. Combining manual and automated verification techniques enhances efficiency and accuracy. Staying updated on regulatory changes and compliance requirements ensures that all transactions meet the necessary financial standards.
Challenges in Audit Tracing and Vouching
Challenges in Audit Tracing
One major challenge in audit tracing is handling a high volume of transactions, which can make it difficult to trace every transaction efficiently. Data integrity issues, such as incomplete or incorrect records, further complicate the process. Additionally, complex financial systems can make tracing transactions across decentralized environments more challenging.
Challenges in Vouching
Vouching also presents challenges, particularly in accessing documents. Sometimes, obtaining original records can be difficult, especially in cases where documentation is missing or unavailable. Detecting fraud is another challenge, as manipulated records can make it harder to identify discrepancies. Time constraints can also limit the ability to verify every transaction in detail.
Tools and Technologies for Audit Tracing and Vouching
Audit Software and Automation Tools
Modern audit software, such as ACL Analytics, IDEA, CaseWare, and TeamMate, can streamline the tracing and vouching processes. Automation minimizes manual effort and reduces errors, improving audit efficiency and accuracy.
Data Analytics and Artificial Intelligence
AI and machine learning enhance audit procedures by identifying patterns, detecting anomalies, and correlating data across multiple sources. These technologies allow auditors to perform more effective tracing and vouching with greater speed and accuracy.
Real-World Applications of Tracing and Vouching
In Financial Audits
Tracing and vouching play a critical role in financial audits, ensuring compliance and accuracy in business transactions. These procedures help maintain transparency and reliability in financial reporting.
In Compliance and Regulatory Audits
Organizations use tracing and vouching to meet regulatory requirements under standards like IFRS, GAAP, and Sarbanes-Oxley (SOX). These methods help ensure compliance and prevent financial misstatements.
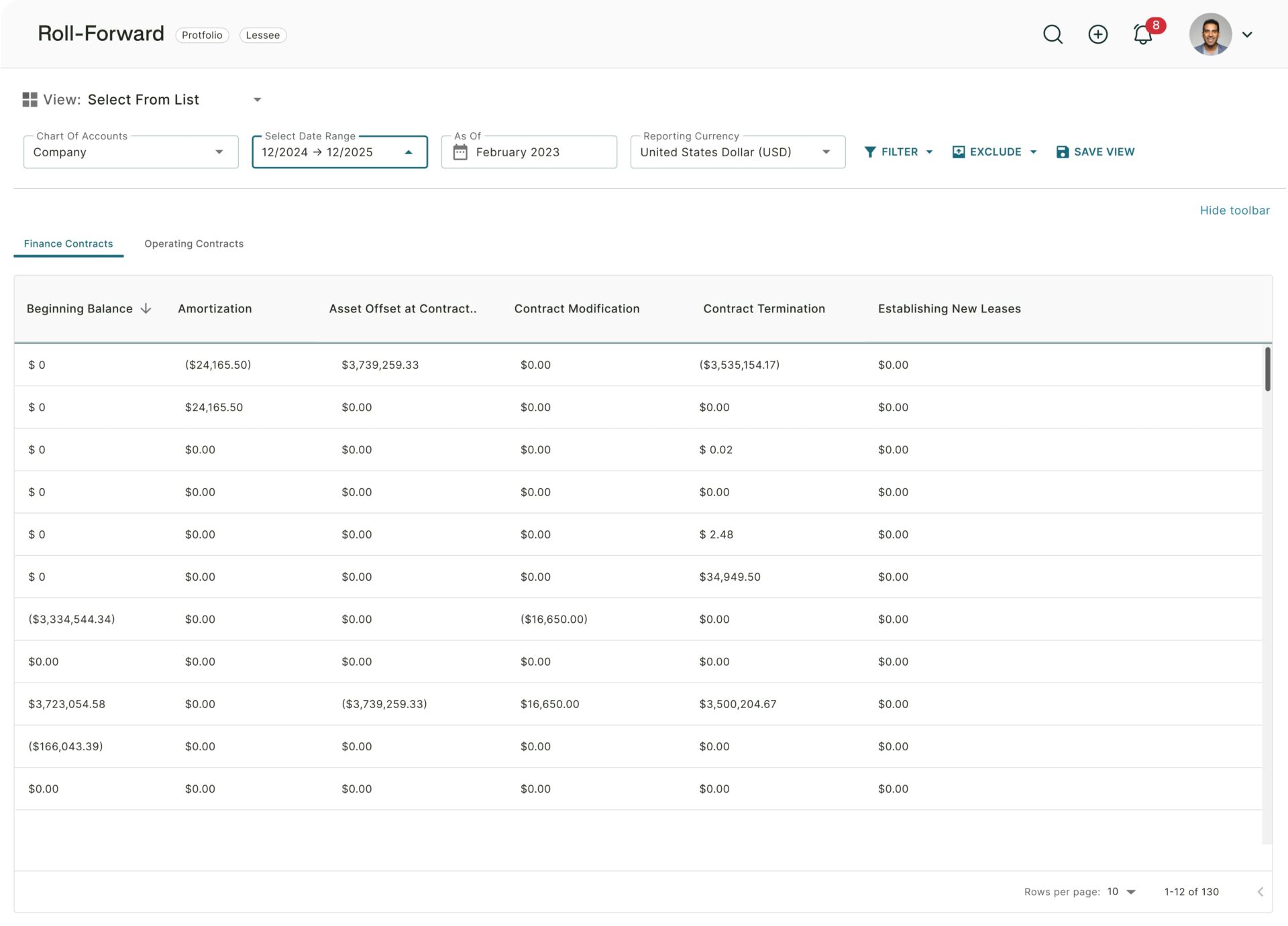
How Trullion Enhances Audit Tracing & Vouching
Trullion’s AI-powered audit tools completely optimize the way auditors conduct tracing and vouching. Its intelligent data reconciliation capability efficiently matches transactions against a repository of source documents using rules-based logic.
It slashes time wasted on tedious data matching, including vouching and tracing. The workflow is simple:
- Upload your documentation: Upload PDF and Excel documents with one-click
- Customize your matching criteria: Customize matching criteria including vendor names, payment amounts, and dates.
- Find matches and exceptions in your data: Trullion’s AI finds matches and exceptions in your data.
How is this used daily by auditors when carrying our audit tracing and vouching?
Test of details: Simplify the process of matching transaction details to critical audit evidence, such as invoices, purchase orders, and payment receipts.
Transaction vouching: Track transactions – including revenue, expenses, tax payments, and payroll – back to supporting documents to confirm accuracy.
Verification and compliance: Validate employee benefit plans, confirm background check completion, and oversee password management to maintain organizational standards.
Fraud prevention: Detect fraud risks in corporate expenses and oversee vendor transactions to ensure proper authorization before payment processing.
Trullion’s data match technology automates vouching by linking accounting records to source documents. Financial statement validation ensures accuracy and consistency in reporting, while AI-powered audit assistance helps identify discrepancies and flag anomalies for review.
Finally, powerful collaboration features allow auditors to work securely with teams and clients, in real-time.
Interested in seeing more? Request a demo to see it in action and ask any questions you might have.
Conclusion: Key Takeaways
As we’ve established, tracing ensures completeness, while vouching verifies authenticity. Both methods are critical for a comprehensive audit, and for providing an opinion on the financial statements.
We also saw how AI and automation improve efficiency and accuracy, and the value that Trullion provides as a cutting-edge solution for audit tracing and vouching.
By leveraging this technology, auditors can focus on strategic insights rather than manual processes – streamlining workflows and delivering higher-quality audits.